Page 50 - 2020 Defence White Paper
P. 50
missiles.
In 2016, North Korea developed Paektusan, an advanced high-yield engine. The development provided
the country with a foundation for the development of nuclear-capable ballistic missiles. In May, August,
and September 2017, North Korea launched a Hwasong-12 Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM).
In July and November 2017, North Korea launched the Hwasong-14 and Hwasong-15 missiles, which
are assessed to be Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs), respectively.
In August 2016, North Korea used the old Soviet Union’s SLBM technology to test-launch an SLBM
(Pukguksong) from a Gorae-class submarine and test-launched in 2017 two Pukguksong-2 missiles as a
ground-to-ground variation. In 2019, North Korea developed and test fired various types of new solid-
propellant short-range ballistic missiles and TELs (both wheeled and tracked) and test-launched the
Pukguksong-3 in October 2, 2019 using the new underwater launch tube.
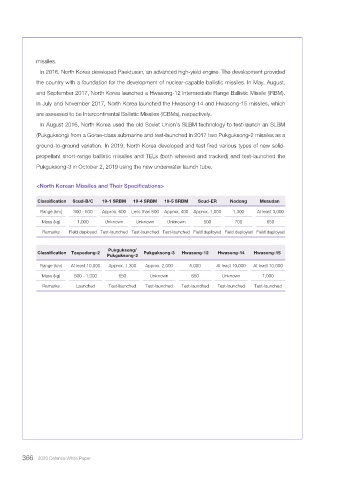
<North Korean Missiles and Their Specifications>
Classification Scud-B/C 19-1 SRBM 19-4 SRBM 19-5 SRBM Scud-ER Nodong Musudan
Range (km) 300 - 500 Approx. 600 Less than 600 Approx. 400 Approx. 1,000 1,300 At least 3,000
Mass (kg) 1,000 Unknown Unknown Unknown 500 700 650
Remarks Field deployed Test-launched Test-launched Test-launched Field deployed Field deployed Field deployed
Pukguksong/
Classification Taepodong-2 Pukguksong-3 Hwasong-12 Hwasong-14 Hwasong-15
Pukguksong-2
Range (km) At least 10,000 Approx. 1,300 Approx. 2,000 5,000 At least 10,000 At least 10,000
Mass (kg) 500 - 1,000 650 Unknown 650 Unknown 1,000
Remarks Launched Test-launched Test-launched Test-launched Test-launched Test-launched
2020 Defense White Paper