Page 317 - 2018 Defense White Paper
P. 317
mounting warheads on missiles, and achieving mass-production. North Korea disabled key nuclear facilities
in Yongbyon during the Six-Party Talks until the end of 2008 and temporarily discontinued the production
of nuclear materials. However, after the talks fell through over disagreement on the verification issue, North
Korea reactivated the nuclear facilities which were in the process of being disabled in 2009 and conducted
the second nuclear test in May. The yield of the explosion in the second test was measured at 3 to 4 kt
representing a significant improvement over the first test. However, the yield of the explosion was still less
than force of the nuclear bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki which led to the assessment that
North Korea’s nuclear capability was lacking in terms of actual employment.
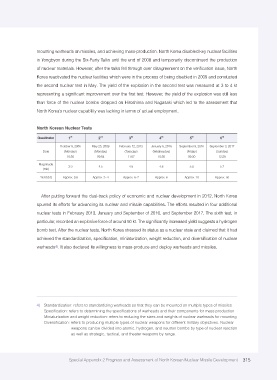
North Korean Nuclear Tests
st nd rd th th th
Classification 1 2 3 4 5 6
October 9, 2006 May 25, 2009 February 12, 2013 January 6, 2016 September 9, 2016 September 3, 2017
Date (Monday) (Monday) (Tuesday) (Wednesday) (Friday) (Sunday)
10:36 09:54 11:57 10:30 09:30 12:29
Magnitude
3.9 4.5 4.9 4.8 5.0 5.7
(mb)
Yield (kt) Approx. 0.8 Approx. 3 - 4 Approx. 6 -7 Approx. 6 Approx. 10 Approx. 50
After putting forward the dual-track policy of economic and nuclear development in 2012, North Korea
spurred its efforts for advancing its nuclear and missile capabilities. The efforts resulted in four additional
nuclear tests in February 2013, January and September of 2016, and September 2017. The sixth test, in
particular, recorded an explosive force of around 50 kt. The significantly increased yield suggests a hydrogen
bomb test. After the nuclear tests, North Korea stressed its status as a nuclear state and claimed that it had
achieved the standardization, specification, miniaturization, weight reduction, and diversification of nuclear
warheads 4) . It also declared its willingness to mass-produce and deploy warheads and missiles.
4) Standardization: refers to standardizing warheads so that they can be mounted on multiple types of missiles
Specification: refers to determining the specifications of warheads and their components for mass production
Miniaturization and weight reduction: refers to reducing the sizes and weights of nuclear warheads for mounting
Diversification: refers to producing multiple types of nuclear weapons for different military objectives. Nuclear
weapons can be divided into atomic, hydrogen, and neutron bombs by type of nuclear reaction
as well as strategic, tactical, and theater weapons by range.
Special Appendix 2 Progress and Assessment of North Korean Nuclear Missile Development 315